Here's an article from eater.com with interesting details on the different marketplace institutions being tried to limit no-shows at high end restaurants...from abolishing reservations, to overbooking, to credit card reservations with penalties, to a theater-ticket model. How Restaurants Can Deal With No-Show Diners
HT: Neil Dorosin (who points out that somewhat similar issues arise in school choice, since schools also suffer from no-shows when the school year begins)
Tuesday, April 30, 2013
Monday, April 29, 2013
Experimental social science conference at Stanford
West Coast Experiments Conference, May 10, register by May 1....http://ps-experiments.ucr.edu/conference/western
WCE.2013, Stanford University: The sixth annual meeting of the West Coast Experiments Conference will be held at Stanford University on Friday, May 10.
We encourage anyone with an interest in experiments to attend; graduate students are especially welcome, as well as those who are new to experimental research. The WCE conference is organized more as a methods "workshop" than as a venue to engage in subfield debates. Presenters focus on one or two methodological take away points of their experimental work. The goal is to give the audience applied, practical advice on methods and design in a way that will help them improve their own experimental research.
The WCE conference is a single day meeting, starting at 9 and ending after dinner. Although we do not have the money to cover travel or lodging expenses, we will provide all meals on that day and we promise a good conversation.
The conference will be held in the Koret Taube Conference Center at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research (SIEPR), located at 366 Galvez Street.
Presentations include (in no particular order):
Social experiments that really matter in the real world:
- Alvin Roth (Stanford Economics): Market design experiments concerning deceased organ allocation (joint work with Judd Kessler)
- Scott Desposato (UCSD Political Science): Ethics in comparative politics experiments
Advances in statistical methods for counterfactual inference:
- Guido Imbens (Stanford Graduate School of Business): Some comments on stratification and re-randomization in randomized experiments
- Luke Keele (Penn State Political Science): Conditioning on posttreatment quantities with structural mean models
Experimental design in political psychology applications:
- Jennifer Merolla (CGU Political Science): Methodological issues surrounding the use of theDynamic Process Tracing Environment (DPTE)
- Eric Dickson (NYU Political Science): "Legitimacy and Enforcement: An Experimental Investigation" (using experimental games to measure psychological quantities and parse psychological mechanisms, joint work with Sandy Gordon and Greg Huber)
- Gabriel Lenz (Berkeley Political Science): Identifying the effect of candidate appearance on vote choice (without assigning candidates to plastic surgery....)
Ted Miguel (Berkeley Economics) also will give an update on the Berkeley Initiative on Transparency in the Social Sciences (BITSS) at lunchtime.
Funding
The conference is made possible by generous funding from the Institute for Research in the Social Sciences at Stanford, the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research, and the Stanford Department of Political Science.
Registration
Registration is free, but you must register by May 1st to be assured of a space at the conference. To register, please click on this link and fill out the required fields.
If you have any questions about registration, please send an email to Jackie Sargent (hijack AT stanford DOT edu)
If you register for the conference but realize later that you need to cancel, please send an email to Jackie and indicate that you wish to cancel your registration.
Parking and Transportation
We have reserved a group of parking spaces near the meeting. We hope participants will carpool to campus. To ensure we have enough for all driving to campus, please contact Jackie Sargent (hijack AT stanford DOT edu) to reserve a space.
Hotel
Hotel: We have reserved a block of rooms at the Sheraton Palo Alto Hotel. Using this link, you may book your own hotel room. The cutoff date for the conference rate is April 19. You also may call the hotel directly and indicate you are with the "West Coast Experiment Conference." Shuttle service to the conference location is available, or it is about a one mile walk.
Participants
This year's co-organizers are:
We will post a spreadsheet with registered participants after the registraion cut-off date.
Contact Information
For more information about the conference, please email Kevin Esterling (kevin DOT esterling AT ucr DOT edu). For information about local arrangements, please contact Jackie Sargent (hijack AT stanford DOT edu; 650.725.1333) or Eliana Vasquez (elianav AT stanford DOT edu; 650.723.8042).
Previous Conferences
May 11, 2012: West Coast Experimental Political Science Conference, UC Berkeley
Conference Program
Conference Program
May 9, 2011: West Coast Experimental Political Science Conference, Caltech
Conference Program
Conference Program
May 21, 2010: West Coast Experimental Political Science Conference, UCLA
Conference Program.
Conference Program.
May 15, 2009: West Coast Experimental Political Science Conference, UCSD
Conference Program
Conference Program
May 2, 2008: Experiments in Political Science, UCR
Conference Program
Conference Program
Sunday, April 28, 2013
Carbon emissions permits are cheap in Europe
The NY Times has the story: In Europe, Paid Permits for Pollution Are Fizzling
"More important, though, than lost jobs and diminished payouts for traders and bankers, the penny ante price of carbon credits means the market is not doing its job: pushing polluters to reduce carbon emissions, which most climate scientists believe contribute to global warming.
"The market for these credits, officially called European Union Allowances, or E.U.A.’s, has been both unstable and under sharp downward pressure this year because of a huge oversupply and a stream of bad political and economic news. On April 16, for instance, after the European Parliament voted down the proposed reduction in the number of credits, prices dropped about 50 percent, to 2.63 euros from nearly 5, in 10 minutes.
“No one was going to buy” on the way down, said Fred Payne, a trader with CF Partners.
"Europe’s troubled experience with carbon trading has also discouraged efforts to establish large-scale carbon trading systems in other countries, including the United States, although California and a group of Northeastern states have set up smaller regional markets.
"Traders do not mind big price swings in any market — in fact, they can make a lot of money if they play them right.
"But over time, the declining prices for the credits have sapped the European market of value, legitimacy and liquidity — the ease with which the allowances can be traded — making it less attractive for financial professionals."
"More important, though, than lost jobs and diminished payouts for traders and bankers, the penny ante price of carbon credits means the market is not doing its job: pushing polluters to reduce carbon emissions, which most climate scientists believe contribute to global warming.
"The market for these credits, officially called European Union Allowances, or E.U.A.’s, has been both unstable and under sharp downward pressure this year because of a huge oversupply and a stream of bad political and economic news. On April 16, for instance, after the European Parliament voted down the proposed reduction in the number of credits, prices dropped about 50 percent, to 2.63 euros from nearly 5, in 10 minutes.
“No one was going to buy” on the way down, said Fred Payne, a trader with CF Partners.
"Europe’s troubled experience with carbon trading has also discouraged efforts to establish large-scale carbon trading systems in other countries, including the United States, although California and a group of Northeastern states have set up smaller regional markets.
"Traders do not mind big price swings in any market — in fact, they can make a lot of money if they play them right.
"But over time, the declining prices for the credits have sapped the European market of value, legitimacy and liquidity — the ease with which the allowances can be traded — making it less attractive for financial professionals."
Saturday, April 27, 2013
The NY Times debates whether prisoners should be able to donate organs
Organ Donors Behind Bars
DEBATERS

The Incarcerated Are Too Vulnerable to Consent
LAWRENCE O. GOSTIN, GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITYDespite rules that organ donations should not affect prisoner conditions, inmates will believe otherwise. Free consent is not truly possible under coercive conditions.
Let Those of Us in Prison Give Life to Others
SHANNON ROSS, INMATE, STANLEY CORRECTIONAL INSTITUTEThe reasons that people cite for not allowing prisoners to donate organs are careless exaggerations that have become obsolete because of medical advancement.
We Must Draw the Line on Death-Row Inmates
AMY L. FRIEDMAN, TRANSPLANT SURGEONAs surgeons, we must avoid conflicts of interest and consistently say, “No, thank you” to organ donation from a prisoner who has been executed.
Let Prisoners Donate Their Organs
SALLY SATEL, AMERICAN ENTERPRISE INSTITUTEIf healthy inmates are sincerely motivated to donate, fully educated about the risks and receive no special treatment in return, how are they not acting voluntarily?
With the Right Safeguards, the Utah Law Is Fine
RUTH FADEN, JOHNS HOPKINS BERMAN INSTITUTE OF BIOETHICSOne huge concern: this new law appears to leave open the possibility that death-row inmates could request to be executed by removal of their vital organs.
It’s Better to Focus on Other Donor Initiatives
BETH PIRAINO, NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATIONNumerous concerns are raised when prisoners wish to donate to strangers, including whether they have access to appropriate medical care after the surgery.
INTRODUCTION
 Nicole Bengiveno/The New York TimesWould the recipient of this organ care whether it came from a prisoner?
Nicole Bengiveno/The New York TimesWould the recipient of this organ care whether it came from a prisoner?
Utah recently became the first state to explicitly permit general prisoners – not death-row inmates – to donate their organs if they die while incarcerated. Should more states have laws like this? Should prisoners be allowed to make live donations to people other than family members? And with nearly 118,000 people in the U.S. waiting for hearts, kidneys, livers and other life-saving transplants, why not include death-row inmates?
READ THE DISCUSSION »Friday, April 26, 2013
Update on those Four Harvard students on the economics job market this year (2012-13)
Back in November I blogged about Nikhil Agarwal, Stephanie Hurder, Scott Kominers, and Johanna Mollerstrom who were on the market, as well as Alex Peysakhovich who decided early to take a postdoc at Yale.
Well, they all got jobs.
Nikhil Agarwal will go to the Economics department at MIT.
Stephanie Hurder will go to the Economics department at Michigan.
Scott Kominers will return to Harvard as a junior fellow.
Johanna Mollerstrom will go to the Economics department at George Mason.
Congratulations to all!
Well, they all got jobs.
Nikhil Agarwal will go to the Economics department at MIT.
Stephanie Hurder will go to the Economics department at Michigan.
Scott Kominers will return to Harvard as a junior fellow.
Johanna Mollerstrom will go to the Economics department at George Mason.
Congratulations to all!
Thursday, April 25, 2013
Fast company
Tickets For Apple’s WWDC 2013 Sell Out In Under 2 Minutes, Compared To 2 Hours In 2012
Tickets for Apple’s annual Worldwide Developer’s Conference went on sale today at 10 AM Pacific, 1 PM Eastern, and as expected, sold out in record time, at just under 2 minutes. Tickets for the developer-focused event at San Francisco’s Moscone West, which features presentations and one-on-one time with Apple’s own in-house engineers, sold out in just two hours in 2012, in under 12 hours in 2011, and in eight days in 2010.
...
This year also marks the first time Apple has provided advance notice regarding when tickets would go on sale, which almost definitely contributed to the faster-than usual sell-out this time around. Imagine a crop of millions of developers around the world hovering over their computers, waiting for the buying process to go live.
The quick sell-out is made more impressive by the fact that sales of the $1,599 tickets were limited to just one per person, and five per organization, tracked by individual Apple ID. During a previous keynote, former CEO Steve Jobs said that there were over 5,000 attendees at the show, which means that Apple potentially just made as much as $8 million in roughly 90 seconds in gross revenue from the event.
Apple’s developer economy is now a massive industry, having paid out $9 billion in total to developers, at a rate now of around $1 billion per quarter. Both iPhone and iPad audiences continue to grow, and Apple’s tablet especially showed tremendous progress during Apple’s most recent fiscal quarter. While Mac sales seem to be either flat or on the decline, the global growth of the iOS user pool more than makes up for that, and iOS as a platform is still the primary revenue driver when it comes to mobile apps and advertising. Combined, those factors mean interest in tickets for WWDC isn’t likely to flag anytime soon.
HT: Joshua Gans
The NRMP fills most positions this year
Here's the NRMP April 2013 post-match press release: Final NRMP® Residency Match 2013 Results Show 99.4 Percent of Positions Filled
Wednesday, April 24, 2013
Skepticism about presumed consent in organ donor registration
Donate Life California posts a skeptical account of proposals to switch from opt in to opt out: An Attractive Concept with Unattractive Results
"72% of Californians and 75% of Americans who can become organ donors actually donate and save lives at the time of their deaths. Second, California’s actual donation rate of 32.3 nDPM (normalized Donors per Million population[iv]) leads the US ‘s 26.1 nDPM and every country in the world except for Spain’s 33.5 nDPM[1] Meanwhile all other countries trail donation in California and the US; whether they have Presumed Consent or Explicit Consent laws."
...
"Most significant in this assessment of PC vs EC is the fact that the European countries that developed and maintain presumed Consent in their laws do not rely on it to actually recover organs. A 2012 survey of practices reports[vi] that donation professionals in all of these countries require family consent prior to recovery of organs. The fact that all countries that have PC laws do not actually rely on the right of the state to take organs speaks to the public trust and autonomy issues that arise when countries seek to claim any type of property, and makes it clear that the variance in donation rates is a function of cultural and operational aspects rather than legal characteristics of their donation programs."
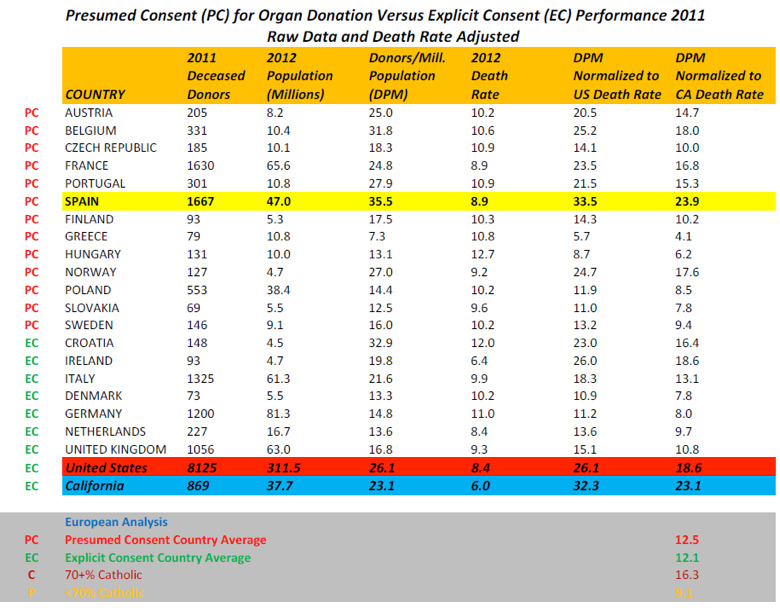
"72% of Californians and 75% of Americans who can become organ donors actually donate and save lives at the time of their deaths. Second, California’s actual donation rate of 32.3 nDPM (normalized Donors per Million population[iv]) leads the US ‘s 26.1 nDPM and every country in the world except for Spain’s 33.5 nDPM[1] Meanwhile all other countries trail donation in California and the US; whether they have Presumed Consent or Explicit Consent laws."
...
"Most significant in this assessment of PC vs EC is the fact that the European countries that developed and maintain presumed Consent in their laws do not rely on it to actually recover organs. A 2012 survey of practices reports[vi] that donation professionals in all of these countries require family consent prior to recovery of organs. The fact that all countries that have PC laws do not actually rely on the right of the state to take organs speaks to the public trust and autonomy issues that arise when countries seek to claim any type of property, and makes it clear that the variance in donation rates is a function of cultural and operational aspects rather than legal characteristics of their donation programs."

Tuesday, April 23, 2013
Gay marriage in France
Here's the story from the Guardian about what appears to be the end to a contentious transition in France from an illegal, repugnant transaction (actually, not just marriage, but also adoption, so two repugnant transactions) to transactions fully sanctioned by law, although still with substantial numbers of opponents:
France approves same-sex marriage: Passing of law allowing gay couples to marry and adopt children comes after heated debate in parliament and weeks of protest
France has become the 14th country to legalise same-sex marriage , pushing through François Hollande's flagship social change after months of street protests, political slanging matches and a rise in homophobic attacks.
After 331 votes for and 225 votes against, there were chants of "Equality. Equality." in the French assembly, where the Socialists have an absolute majority. But thousands of riot police and water cannons were in place near the parliament building in Paris in advance of planned demonstrations against the law.
The right to marriage and adoption for everyone regardless of sexual orientation has proved bitterly divisive in France, triggering the biggest conservative and rightwing street protests in 30 years. Recent weeks have seen more than 200 arrests as police teargassed late-night demonstrators near parliament. More than 172 hours of heated debate in the assembly and the senate meant the bill was one of the most debated in recent history, with furious clashes and a near fist-fightbetween politicians.
One rightwing MP warned the government was "killing children" by allowing same-sex married couples to adopt and one senator warned gay marriage would open the way to people being able to marry animals or objects. MPs in favour of the bill received death threats, skinheads attacked a gay bar in Lille, and gay rights groups reported a rise in homophobic attacks.
Before the vote, the speaker of the assembly ordered the expulsion of noisy protesters from the public gallery, calling them "enemies of democracy".
The vote makes France the ninth country in Europe to legalise same-sex marriage and the first ceremonies could take place this summer.
Crick's Nobel medal, and letter to his son describing DNA
For those of you have been waiting for news since I posted about the auction of Francis Crick's Nobel medal, wait no longer: How Much is a Nobel Prize Worth? If It’s Francis Crick’s, the Answer is $2 Million
Even better, his letter to his 12 year old son describing DNA sold for six million: you can read the whole letter here
...
...
Even better, his letter to his 12 year old son describing DNA sold for six million: you can read the whole letter here
...
...
Monday, April 22, 2013
Recommender algorithms for labor market search
Aki Ito has written a nice story at Bloomberg News about ongoing efforts to design labor market search engines to deal with congestion: Algorithms Play Matchmaker to Fight 7.7% U.S. Unemployment: Jobs
She writes about sites like AfterCollege and CareerBuilder and Burning Glass, as well as the online IT marketplace ODesk.
There's a lot going on in labor market matching and matchmaking, and lots of good market design problems in that space.
She writes about sites like AfterCollege and CareerBuilder and Burning Glass, as well as the online IT marketplace ODesk.
There's a lot going on in labor market matching and matchmaking, and lots of good market design problems in that space.
Sunday, April 21, 2013
Is freedom to do social science research like freedom of the press?
A group of British social scientists (who appear to mostly be involved in survey research) think that the current system of institutional review of research in Britain is better suited to medical experiments than to social science.
Here's the story:
Read more: http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2013/03/14/british-social-scientists-propose-new-approach-ethics-review#ixzz2NYEV2Xos
Inside Higher Ed
Here's the story:
Social Science Ethics
March 14, 2013 - 3:00am
British social scientists are drawing up a common set of ethical principles aimed at freeing research from what they see as excessive ethics oversight frameworks that hamper their ability to improve social understanding.
According to Robert Dingwall, professor of social science at Nottingham Trent University, a "free" social science research base is as important to a healthy democracy as a free press. But in the past decade, British and international funders have required universities to vet all research involving human subjects via institutional ethics committees.
"You can imagine how outraged journalists would feel if they had to pre-check with a committee that their questions would not upset someone," he said.
Dingwall, a member of an Academy of Social Sciences working group on the issue, said committee members often had no expertise in ethics or the research field in question, and were primarily concerned with the university's reputation. Their risk aversion fed back to academics, who were often disinclined to undertake research that could incur disapproval even if it was potentially important.
The situation was exacerbated, Dingwall said, by the application to social science of frameworks developed for biomedicine. He said the balance of individual risk and social benefit was different in the social sciences because most research posed a minimal risk to individuals and offered significant benefit to the community.
He said that although the U.S. and Canada have recognized that the regulatory system was in crisis, Britain has yet to join efforts to redress it.
Read more: http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2013/03/14/british-social-scientists-propose-new-approach-ethics-review#ixzz2NYEV2Xos
Inside Higher Ed
Saturday, April 20, 2013
Paul Milgrom's Wikipedia page (and 65th birthday present)
Today is Paul Milgrom's 65th birthday, and is the second day of a conference in his honor that has brought his students and other admirers from all over the world. Joshua Gans led the creation of the birthday present, which involved bringing Paul Milgrom's Wikipedia page up to snuff. As Joshua announced at the dinner last night, it is presently the longest Wikipedia page for any living economist (maybe for any economist, I didn't get that clear...). Here's a picture of it being presented to Paul in scroll form, held up by those of his students who were present:
It's a great celebration of Paul's remarkable career, at its midpoint.
Happy birthday, Paul.
 |
| Paul' Milgrom's Wikipedia page, printed out for his birthday |
It's a great celebration of Paul's remarkable career, at its midpoint.
Happy birthday, Paul.
 |
| Paul Milgrom, rebutting all the toasts in his honor |
Friday, April 19, 2013
Conference in Honor of Paul Milgrom's 65th Birthday
Paul Milgrom is a giant, not just in market design, and at 65 he's still going full blast. Here's the program for his birthday party:
Program: Conference in Honor of Paul Milgrom's 65th Birthday
Location: Landau economics, first floor
Friday, April 19
Introduction to Conference
10:30-10:45 Susan Athey, Yeon-Koo Che and Joshua Gans
Session 1: Market Design Methods in Matching and Auctions
10:45-10:55 a.m. Al Roth: Introduction
10:55-11:25 a.m. John Hatfield: “Matching with Contracts”
11:25-11:35 a.m. coffee break
11:35-12:05 p.m. Yeon-Koo Che: “Generalized Reduced Form Auctions: A Network-Flow Approach,” with Jinwoo Kim and Konrad Mierendorff
12:05-12:35 p.m. Paul Klemperer: “Geometry, Auctions, and Matching”
Lunch
12:35-1:35 p.m.
Session 2: Auctions and Market Design
1:35-1:45 p.m. Preston McAfee: Introduction
1:45-2:15 p.m. Lixin Ye: "Efficient and Optimal Mechanisms with Private Information Acquisition Costs," with Jingfeng Lu
2:45-3:00 p.m. Coffee Break
3:00-3:30 p.m. David McAdams, "Secrecy in the First-Price Auction".
3:30-4:00 p.m. Ilya Segal, “U.S. Spectrum Reallocation and Heuristic Auctions,” with Paul Milgrom.
4:00-4:15 p.m. Coffee Break
Panel Discussion: Market Design in Practice
4:15-5:00 p.m. Panel Discussion
Dinner
Vidalakis Dining Room, Schwab Center
6:30 p.m. Appetizers
7:15 p.m. Seated dinner begins serving
Saturday, April 20
Breakfast
9 a.m. at conference site
Session 3: Organizations and Complementarity
9:30-9:40 a.m. John Roberts: Introduction
9:40-10:10 a.m. Nick Bloom: Management and Organizations
10:10-10:40 a.m. Bruno Strulovici: "The Supermodular Stochastic Ordering," with Margaret Meyer
10:40-11:00 a.m. Coffee Break
Session 4: Incentives and Games
11:00-11:15 a.m. Bengt Holmstrom: Introduction and Retrospective on Static and Multitask Incentive Theory
11:15-11:45 a.m. Andy Skrzypacz: Repeated games and incentives
11:45-12:15 p.m. Michi Kandori: How to cooperate under private monitoring
12:15-1:15 p.m. Lunch
Time/Location TBD Afternoon Hike
6:30 p.m. Informal Dinner
Thursday, April 18, 2013
Someone was pretending to be me on Google+ (a story with a happy ending)
The internet is home to a variety of scams, and some of them involve trying to manipulate Google search results. So I was surprised and dismayed, but not entirely shocked, when I noticed that someone was pretending to be me, by establishing a Google+ page for a company called Market Design, whose web page was....this blog.
What could be in it for them? Well, maybe they were really trying to pretend that by hiring them you were hiring me. But maybe they just were moving up in Google searches through the links that this blog gets. Here's what you saw if you searched for "market design" on Google:
The first result, on the left, is my blog. But there's an item under it called "Google+ page" and an address, which both link to the spoofer, who is also on the right, with a phone number and a map, and a picture that if you click on it gets you to one of my blog posts.
If you clicked on the link that says Google+ page under the link to my blog, you got to this page, on which my blog URL was clearly displayed as the company web page:
On 4/7/13 I filled out a problem report on the Google+ profile page, and I wrote a review disclaiming any connection between their site and me or my blog...
Apparently Google pays attention to this kind of complaint. When I checked back on 4/9/13 the spoofer was already nowhere to be found.
A recent email confirmed this:
What could be in it for them? Well, maybe they were really trying to pretend that by hiring them you were hiring me. But maybe they just were moving up in Google searches through the links that this blog gets. Here's what you saw if you searched for "market design" on Google:
The first result, on the left, is my blog. But there's an item under it called "Google+ page" and an address, which both link to the spoofer, who is also on the right, with a phone number and a map, and a picture that if you click on it gets you to one of my blog posts.
If you clicked on the link that says Google+ page under the link to my blog, you got to this page, on which my blog URL was clearly displayed as the company web page:
On 4/7/13 I filled out a problem report on the Google+ profile page, and I wrote a review disclaiming any connection between their site and me or my blog...
Apparently Google pays attention to this kind of complaint. When I checked back on 4/9/13 the spoofer was already nowhere to be found.
A recent email confirmed this:
From: Google Maps [mailto:noreply-local-issues@google.com]
Sent: Tuesday, April 16, 2013 1:09 PM
To: Roth, Alvin
Subject: Google Maps Problem Report - Action taken
Wednesday, April 17, 2013
Bangladesh protesters demand blasphemy law with death penalty for bloggers
One repugnant transaction isn't repugnant enough for protesters in Bangladesh:
Bangladesh protesters demand blasphemy law
"Hundreds of thousands of marchers call for law that would include death penalty for bloggers who they say insult Islam."
"The religious group, which has the backing of country's largest party Jamaat-e-Islami, organised the rally in support of its 13-point demand including enactment of a blasphemy law to prosecute and hang what they call atheist bloggers.
...
"Under the country's cyber laws, a blogger or Internet writer can face up to ten years in jail for defaming a religion."
Bangladesh protesters demand blasphemy law
"Hundreds of thousands of marchers call for law that would include death penalty for bloggers who they say insult Islam."
"The religious group, which has the backing of country's largest party Jamaat-e-Islami, organised the rally in support of its 13-point demand including enactment of a blasphemy law to prosecute and hang what they call atheist bloggers.
...
"Under the country's cyber laws, a blogger or Internet writer can face up to ten years in jail for defaming a religion."
Tuesday, April 16, 2013
Interview with the late Dr Joseph Murray, about the first kidney transplants and related matters
Great interview, conducted in 2000. Lots of detail. For example, he practiced on dogs, removing a dog's kidney and then transplanting it into the same dog, to practice the surgical techniques for kidney transplants without immunological complications...and discussion of repugnance... and of the generosity and courage of early transplant patients ...and the relationship between basic and applied science (18 minutes for the whole thing).
Here's the video from the Nobel site (I can't figure out how to upload it): http://www.nobelprize.org/mediaplayer/index.php?id=732 .
Here are my earlier posts on Dr. Murray who shared the 1990 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for "...discoveries concerning organ and cell transplantation in the treatment of human disease"
Here's the video from the Nobel site (I can't figure out how to upload it): http://www.nobelprize.org/mediaplayer/index.php?id=732 .
Here are my earlier posts on Dr. Murray who shared the 1990 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for "...discoveries concerning organ and cell transplantation in the treatment of human disease"
Monday, April 15, 2013
Clerkship hiring: early, and concentrated at top schools...
Above the Law reports on Which Law Schools Had the Most Clerkship Placements? and
Clerkship Hiring Is Getting Earlier and Earlier
Here's a quick look at which schools are doing well at placing students into clerkships...

As for earlier and earlier hiring following the recent abandonment of the most recent timetable by the DC Circuit, here are two announcement over at OSCAR (the Online System for Clerkship Application and Review):
As it happens, a new model of unraveling of markets just came by email:
STRATEGIC UNCERTAINTY AND UNRAVELING IN MATCHING
MARKETS, by FEDERICO ECHENIQUE AND JUAN SEBASTIAN PEREYRA
From their introduction:
"Strategic unraveling in our model proceeds as follows. There is a loss in efficiency when some agents go early: Information about the quality of the matches arrives late, so it is better for efficiency to wait until the information has arrived to make a match. If some agents go early anyway, this forces later matches to be less efficient. The result is a negative externality that makes it more tempting for all agents to go early. It may push some additional agents over the threshold by which they decide to go early. In turn, these additional agents going early makes it even more tempting to go early|and so on and so forth."
Clerkship Hiring Is Getting Earlier and Earlier
Here's a quick look at which schools are doing well at placing students into clerkships...

As for earlier and earlier hiring following the recent abandonment of the most recent timetable by the DC Circuit, here are two announcement over at OSCAR (the Online System for Clerkship Application and Review):
Latest OSCAR News
RSS
Federal Law Clerk Hiring Plan Date Change
Apr 10, 2013 4:30 pm
The OSCAR system will release all online third-year law school student applications on June 28, 2013 at 12:00 pm Noon (EDT).
OSCAR Version 7: Limit of 100 Clerkship Applications
Apr 08, 2013 11:10 am
To address judge concerns, Version 7 introduces a 100-application limit per applicant for clerkship applications.As it happens, a new model of unraveling of markets just came by email:
STRATEGIC UNCERTAINTY AND UNRAVELING IN MATCHING
MARKETS, by FEDERICO ECHENIQUE AND JUAN SEBASTIAN PEREYRA
From their introduction:
"Strategic unraveling in our model proceeds as follows. There is a loss in efficiency when some agents go early: Information about the quality of the matches arrives late, so it is better for efficiency to wait until the information has arrived to make a match. If some agents go early anyway, this forces later matches to be less efficient. The result is a negative externality that makes it more tempting for all agents to go early. It may push some additional agents over the threshold by which they decide to go early. In turn, these additional agents going early makes it even more tempting to go early|and so on and so forth."
Internal exchanges in financial markets
The NY Times has a story on the increasing volume of trade going on in "dark pools," as opposed to in public exchanges. As Market Heats Up, Trading Slips Into Shadows. One point it makes is that some funds feel the exchanges aren't as safe as they used to be, e.g. because of high frequency traders.
The passage I found most interesting however, was about intercepting the trades of small investors before they get to exchanges:
"Other places besides the 30-plus dark pools are stealing the business of stock exchanges. A handful of firms including Citigroup and Knight Capital pay retail brokers like TD Ameritrade and Scottrade for the opportunity to trade with ordinary retail investors before the orders can reach an exchange, a phenomenon known as internalization. This type of off-exchange trading has also been growing, in part because of the recent revival of interest in the stock market among ordinary investors."
This is a little bit like what we are seeing in kidney exchange, in which big transplant centers withhold their easy to match pairs and transplant them internally. See e.g.
Ashlagi, Itai and Alvin E. Roth, "New challenges in multi-hospital kidney exchange," American Economic Review papers and proceedings, May 2012, 102,3, 354-59
The passage I found most interesting however, was about intercepting the trades of small investors before they get to exchanges:
"Other places besides the 30-plus dark pools are stealing the business of stock exchanges. A handful of firms including Citigroup and Knight Capital pay retail brokers like TD Ameritrade and Scottrade for the opportunity to trade with ordinary retail investors before the orders can reach an exchange, a phenomenon known as internalization. This type of off-exchange trading has also been growing, in part because of the recent revival of interest in the stock market among ordinary investors."
This is a little bit like what we are seeing in kidney exchange, in which big transplant centers withhold their easy to match pairs and transplant them internally. See e.g.
Ashlagi, Itai and Alvin E. Roth, "New challenges in multi-hospital kidney exchange," American Economic Review papers and proceedings, May 2012, 102,3, 354-59
Sunday, April 14, 2013
Buying a place in line to hear Supreme Court arguments
Over at the Volokh Conspiracy Dale Carpenter has the story, and the URL is more informative than the headline: http://www.volokh.com/2013/03/30/misbehavior-at-the-court/
"There are actually two lines to get into the chamber, which has very limited seating capacity. One is for the general public, and in high-profile cases it’s quite long. The other is for lawyers who become members of the Supreme Court bar. Bar members enjoy a limited number of reserved seats at the front of the audience, right behind the lawyers for the parties in the case. ...
"There are actually two lines to get into the chamber, which has very limited seating capacity. One is for the general public, and in high-profile cases it’s quite long. The other is for lawyers who become members of the Supreme Court bar. Bar members enjoy a limited number of reserved seats at the front of the audience, right behind the lawyers for the parties in the case. ...
I joined the Supreme Court bar ($200 one-time fee) in order to get into the marriage arguments. I knew the lines would be long, so I arrived Tuesday morning at about 3:15 a.m., thinking that would be good enough to get me in. I was about 57th in line at that point for about 100 seats in the bar section. In front of me were mostly paid line-standers who had been waiting in the 30-degree temperatures all night. I talked with quite a few of them. None were members of the bar. Almost all were impoverished and black. Many of them slept on the ground, in cold and wet conditions, for several nights.
As daylight approached, a lot of equality advocates arrived to take their premium places in line. These “clients,” as the line-standers called them, paid about $50 an hour to line-standing-service middlemen organized as businesses (I don’t know what the actual line-standers earn per hour). For the Prop 8 case, it cost as much as $6,000 to get to the front of the line and guarantee a seat in the courtroom. Neither the Supreme Court nor any law-enforcement authorities prohibit this practice.
I don’t categorically object to line-placement capitalism, especially for private functions like buying tickets to a rock concert. It’s an economic exchange in which the highest bidders get what they want and others sell their services and earn money they wouldn’t otherwise get. It does seem odd to hold what’s effectively a private-market auction for seats at a public hearing of the country’s highest court. Many of the buyers who participated in this particular market, given what I know of their other political preferences, would be hard put to defend this system in a public forum.
They started letting us into the Court at about 7:30 for the Prop 8 argument on Tuesday. I got into the main room, third row from the front, not more than 50 feet from the Justices. Getting there early — and being able to stand in a separate bar-members line – had paid off.
But what happened the next day for the DOMA argument was appalling. I arrived at 2:15 a.m. when the temperature was a balmy 40 degrees and was headed down. I was 46th in line, again with a group consisting almost entirely of paid line-standers in front of me. There were very few bar members personally waiting in line at that time. The Court had space for fewer bar members that day in order to make room for an extra table for counsel arguing the jurisdictional issues. But even with more limited seating, #46 was still sure to get in.
As 7 a.m. approached and the lawyers arrived to take their pre-paid places in line, something else happened. They started inviting their friends to join them at the front of the line, pushing back people who had waited all night to get in. The lawyer-clients of several of the line-standers near me never arrived to relieve their assigned line-standers, no doubt because they cut in line further up than what they had paid for. Pretty soon, I was #55 and then #65 and then I lost count. "
Saturday, April 13, 2013
Robert Edwards, R.I.P. Brought in vitro fertilization from repugnant transaction to Nobel prize
Robert G. Edwards Dies at 87; Changed Rules of Conception With First ‘Test Tube Baby’
"Working with Dr. Patrick Steptoe, Dr. Edwards essentially changed the rules for how people can come into the world. Conception was now possible outside the body — in a petri dish.
"The technique has resulted in the births of five million babies, many in multiple births, according to the International Committee Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies, an independent nonprofit group.
"Yet, like so many pioneers of science, Dr. Edwards and Dr. Steptoe achieved what they did in the face of a skeptical establishment and choruses of critics, some of whom found the idea of a “test tube baby” morally repugnant. Denied government support, the two men resorted to private financing. And they did their work in virtual seclusion, in a tiny, windowless laboratory at a small, out-of-the-way English hospital outside Manchester.
"It was there, after outwitting a crowd of reporters, that they delivered their — and the world’s — first IVF baby, Louise Brown, on July 25, 1978. Her parents, John and Lesley Brown, had tried for nine years to have a child — a period that virtually coincided with Dr. Edwards’s research."
*****************
Here's my earlier post on the occasion of his Nobel, including some dissenting voices at the time:
"Working with Dr. Patrick Steptoe, Dr. Edwards essentially changed the rules for how people can come into the world. Conception was now possible outside the body — in a petri dish.
"The technique has resulted in the births of five million babies, many in multiple births, according to the International Committee Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies, an independent nonprofit group.
"Yet, like so many pioneers of science, Dr. Edwards and Dr. Steptoe achieved what they did in the face of a skeptical establishment and choruses of critics, some of whom found the idea of a “test tube baby” morally repugnant. Denied government support, the two men resorted to private financing. And they did their work in virtual seclusion, in a tiny, windowless laboratory at a small, out-of-the-way English hospital outside Manchester.
"It was there, after outwitting a crowd of reporters, that they delivered their — and the world’s — first IVF baby, Louise Brown, on July 25, 1978. Her parents, John and Lesley Brown, had tried for nine years to have a child — a period that virtually coincided with Dr. Edwards’s research."
*****************
Here's my earlier post on the occasion of his Nobel, including some dissenting voices at the time:
From repugnant transaction to Nobel Prize in Medicine
Friday, April 12, 2013
Law schools forming law firms to employ new graduates
The NY Times has the story. The quote is from the dean of the Arizona State U. Law School: To Place Graduates, Law Schools Are Opening Firms
"“I realized that was what we needed,” Mr. Sylvester recalled. “A teaching hospital for law school graduates.”
"The result is a nonprofit law firm that Arizona State is setting up this summer for some of its graduates. Over the next few years, 30 graduates will work under seasoned lawyers and be paid for a wide range of services provided at relatively low cost to the people of Phoenix."
"“I realized that was what we needed,” Mr. Sylvester recalled. “A teaching hospital for law school graduates.”
"The result is a nonprofit law firm that Arizona State is setting up this summer for some of its graduates. Over the next few years, 30 graduates will work under seasoned lawyers and be paid for a wide range of services provided at relatively low cost to the people of Phoenix."
Thursday, April 11, 2013
The economics of designing markets, and the sociology of "civilizing" them
Jose Ossandon emailed me to alert me about his thoughtful blog post comparing some developments in market design and in the sociology of markets. In particular, he draws connections between market design and some of the work of Michel Callon.
Ossandon's blog post is called Are markets matching Callon and Roth?
He begins:
"The last meeting of our “Copenhagen market group”[i] was devoted to an increasingly influential stream within current economics, namely “market design”. The discussion left me with the somehow perplexing puzzle I am trying to unfold in this post: isn’t this type of economics almost too close to the ‘markets as calculative collective devices’[ii] approach developed by Michel Callon and colleagues so influential among us -non-economists market researchers- in the last years?
I haven't yet had a chance to do more than glance at the links he provides: it's clear that some translation will be needed between econ and soc, in order for me to try to understand all the connections that he sees.
Ossandon's blog post is called Are markets matching Callon and Roth?
He begins:
"The last meeting of our “Copenhagen market group”[i] was devoted to an increasingly influential stream within current economics, namely “market design”. The discussion left me with the somehow perplexing puzzle I am trying to unfold in this post: isn’t this type of economics almost too close to the ‘markets as calculative collective devices’[ii] approach developed by Michel Callon and colleagues so influential among us -non-economists market researchers- in the last years?
During the meeting we discussed two articles (here and here) written by the 2012 Nobel Prize winner Alvin Roth. As Roth explains, see also his very clear Nobel Prize speech, his and his colleagues’ work has been dedicated to very practical problems."
"Are the new2 economic sociology and market design the same? Avoiding the obvious methodological splits that separate a highly formalized and a rather descriptive-reflexive ethnographic approach, there are still important conceptual differences. The ideal situation for Roth’s designers seems to be “give me some choosing things[iii] to match and I will rise a technologically equipped market”, while for Callon - especially in his work connecting his thoughts on technical democracy, hybrid forums and markets- the ideal situation is where what is traded, who can participate in the exchange, and who and what is equipping the market encounter are collectively and heterogeneously defined. Civilizing (Callon) and engineering (Roth) markets are therefore two different programs of market design. More practically, for instance, in school choice, for Roth et al. what a good school is or who can choose or what is chosen while matching school places is defined before the market. In Callon et al.’s view such an arrangement would not only match pre-calculating families and schools but it would include the consequence of making the involved agents calculative, changing accordingly the way they understand and deal with education. In other words, in Callon’s view markets are never only about matching, or matching would need to beunderstood also as a mode of per-formatting new agencies and things.
But, despite these differences, it seems like finally engineer economists and engineer sociologists are finding a common starting point. Isn’t that scary? I don’t think so. This is a much better place to start and try a dialogue that is not so limited by pre-existing disciplinary boundaries (see also Callon here). Let’s agree: markets are not pre-social metaphysical forces that need to be left alone, but they are practical arrangements that can be more or less, better or worse, designed[iv]. In those cases where there is an already functioning market or quasi-market mechanisms (for instance: school choice or carbon trade) let’s try to make them work the best we can. In other words, social researchers should not only criticize marketization but also spend time, energy and knowledge onengineering and/or civilizing these complex arrangements. This is, I think, a nice pragmatic starting point for market researchers at large.
But is this just good? No it isn’t, there is also a serious flaw. These two streams of market research seem to share a somewhat excessive optimism about markets as devices that can solve social and environmental issues. As a product of neoliberal Chile, I would happily pay for not having to make choices in areas like health insurance, pension funds, schools or long distance phone carriers. And certainly many people have argued that these and other sectors (have you heard about trains in the UK?) are not necessarily working better years after features such as competition, choice and providers able to select or exclude their potential users have been introduced. Market design risks becoming the face of the latest round of social and environmental reforms (for instance: emissions trading or the announced Job Match interface in the UK). And the new reformers seem to believe something like: it is not that markets were necessarily a bad social policy but that they were not properly designed. But, shouldn’t we also be experimenting with other ways of doing things? I am not saying that markets are always bad, but that the same brilliant ideas currently oriented at designing better markets could also be spent devising other forms of solving our common problems. In my opinion market civilizers and engineers will become fully respectable technicians the day they are also able to advise something like: “thank you for contacting me, but here you don’t need a market”."
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)







