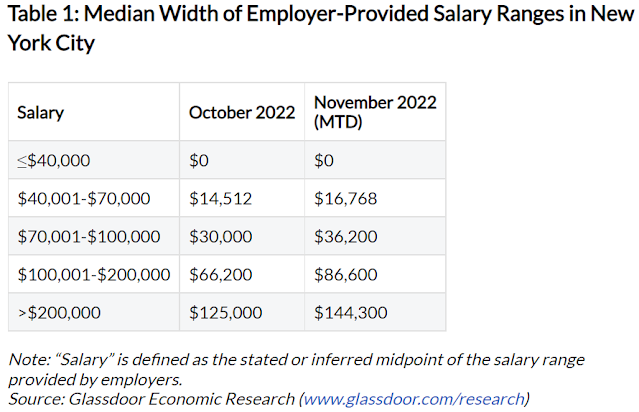
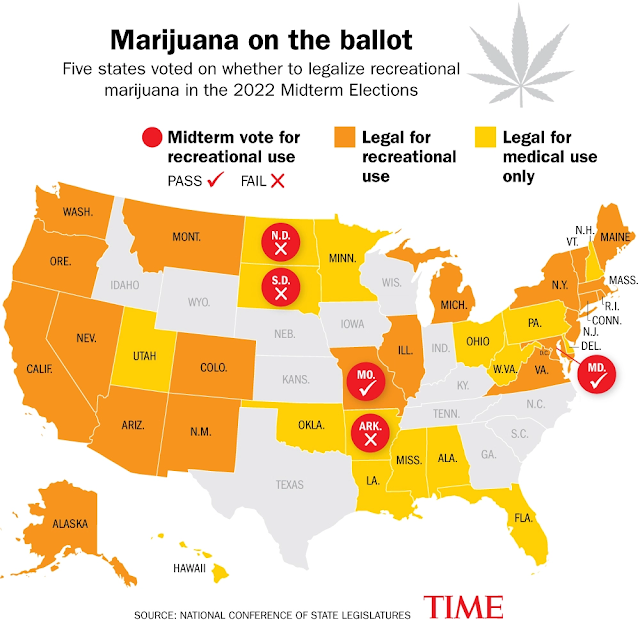
Concerned over the opioid addiction epidemic in the U.S., and the increasing number of overdose related deaths, the CDC issued the 2016 CDC Opioid Prescribing Guideline, which led to reduced opioid prescriptions by doctors. Sometimes this led to the undertreatment of pain, which in turn may have led to patients accessing opioids on the black market, where they are less safe. It may also have led to suicides of patients with unbearable pain.
The CDC has now issued some updated guidelines that appear aimed at balancing concerns with over-prescription against concerns with under-treatment.
Here are the updated guidelines:
CDC Clinical Practice Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Pain — United States, 2022
"This guideline provides recommendations for clinicians providing pain care, including those prescribing opioids, for outpatients aged ≥18 years. It updates the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain — United States, 2016 (MMWR Recomm Rep 2016;65[No. RR-1]:1–49) and includes recommendations for managing acute (duration of <1 month), subacute (duration of 1–3 months), and chronic (duration of >3 months) pain.
...
"CDC recommends that persons with pain receive appropriate pain treatment, with careful consideration of the benefits and risks of all treatment options in the context of the patient’s circumstances. Recommendations should not be applied as inflexible standards of care across patient populations. This clinical practice guideline is intended to improve communication between clinicians and patients about the benefits and risks of pain treatments, including opioid therapy; improve the effectiveness and safety of pain treatment; mitigate pain; improve function and quality of life for patients with pain; and reduce risks associated with opioid pain therapy, including opioid use disorder, overdose, and death.
A central tenet of this clinical practice guideline is that acute, subacute, and chronic pain needs to be appropriately and effectively treated regardless of whether opioids are part of a treatment regimen.
...
"To avoid unintended consequences for patients, this clinical practice guideline should not be misapplied, or policies derived from it, beyond its intended use (67). Examples of misapplication or inappropriate policies include being inflexible on opioid dosage and duration, discontinuing or dismissing patients from a practice, rapidly and noncollaboratively tapering patients who might be stable on a higher dosage, and applying recommendations to populations that are not a focus of the clinical practice guideline (e.g., patients with cancer-related pain, patients with sickle cell disease, or patients during end-of-life care)
*********
Earlier post:
Tuesday, March 15, 2022